General Optics
SWDM, CWDM, LWDM Z-BLOCKs
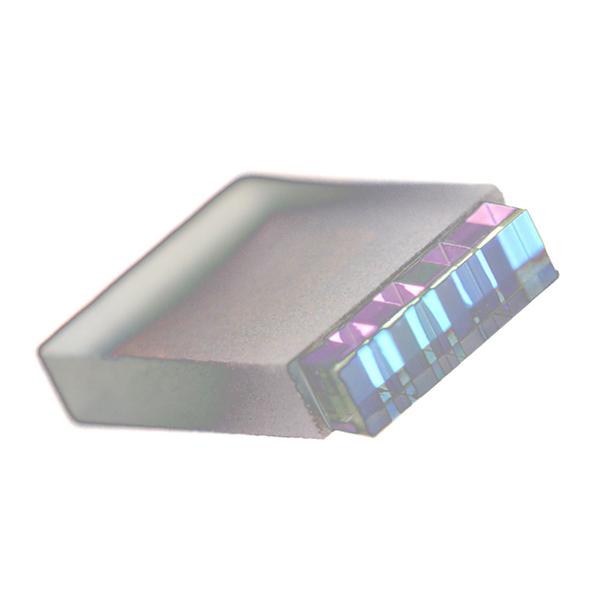
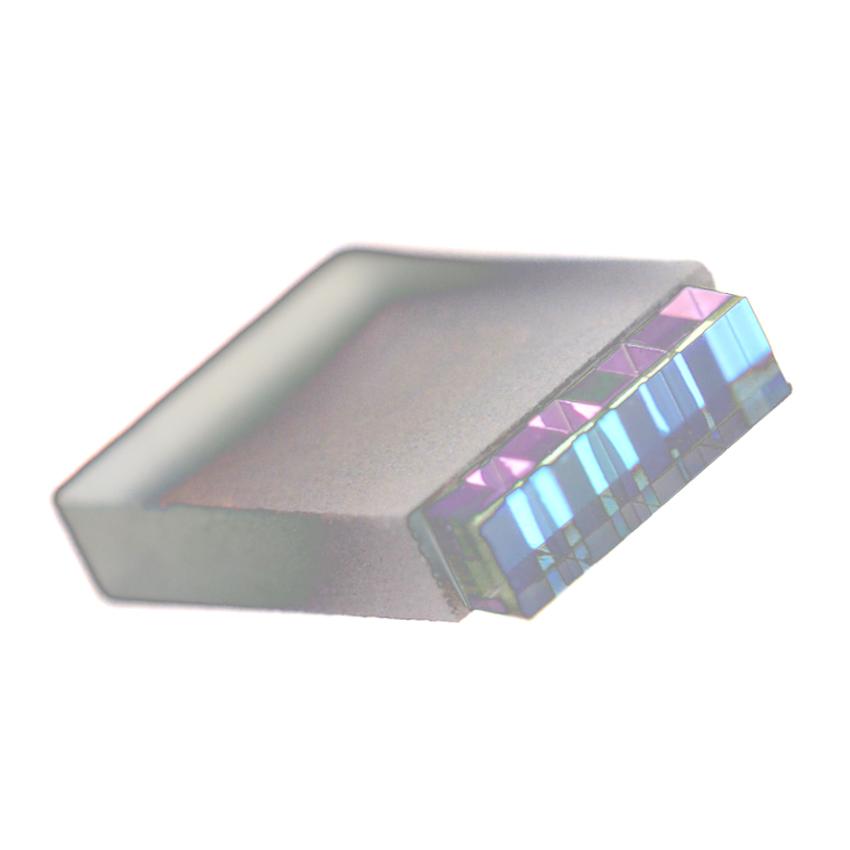
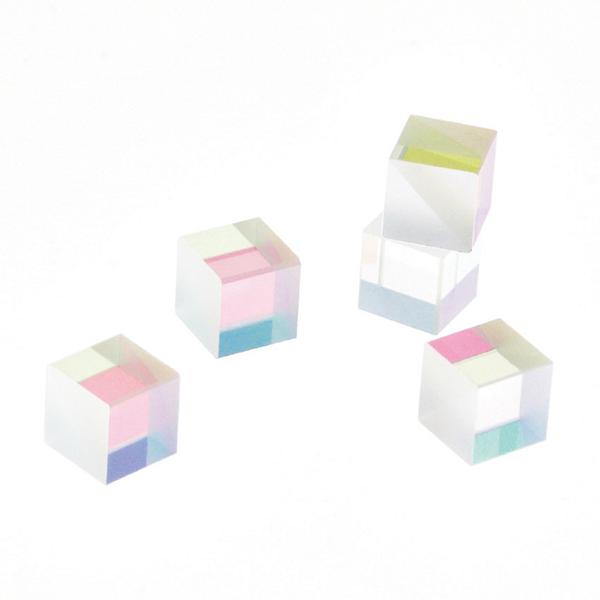
Speed up the assembly of mux/demux components for high-speed optical transceivers with these monolithic Z-blocks that enable a more rapid alignment process.
Coherent Z-block subassemblies deliver a very low insertion loss solution for efficient wavelength multiplexing and demultiplexing in 100G, 400G, 800G systems, and their very high parallelism and pitch tolerances simplify coupling and assembly.
SWDM, CWDM, LWDM Z-BLOCK Specifications
Pick Z-blocks based on the specifications in the table, or specify a custom filter pitch design.
Parameters |
Unit |
CWDM4 |
LAN-WDM |
Operation Wavelength |
nm |
1250-1350 |
1280-1330 |
Center Wavelength (λc) |
nm |
1271/1291/1311/1331 |
1295.56/1300.05/1304.56/1309.14 |
Passband (PB) |
nm |
>λc ± 6.5 |
>λc ± 1.05 |
Max. Insertion Loss @ PB |
dB |
<1.0 |
<1.0 |
IL Uniformity @ PB |
dB |
<0.4 |
<0.5 |
PDL @ Passband |
dB |
<0.25 |
<0.25 |
Adjacent CH Isolation |
dB |
>25 |
>25 |
Non-Adj. CH Isolation |
dB |
>30 |
>30 |
Typical AOI (in air) |
degree |
8/13.5 |
8/13 |
Pitch |
μm |
500/750/900/1000/1100/1500 |
|
Beam Parallelism |
degree |
<0.2 |
<0.2 |
Operating Temperature |
°C |
-20 ~ 85 |
-5 ~ 75 |
Storage Temperature |
°C |
-40 ~ 85 |
-40 ~ 85 |
Related Products
Whitepaper
SWDM: The Lowest Total Cost Solution for 40G/100G in the Enterprise Data Center
Large- and medium-sized enterprises have been widely deploying 10G Ethernet for several years. Their data center infrastructure has been primarily architected around duplex OM3 and OM4 multimode fiber (MMF), since most of the switch port interfaces are multimode 10GBASE-SR using the SFP+ transceiver form factor.

Optical Manufacturing Capabilities
Learn about the vertically integrated capabilities for material growth, fabrication, coating, and assembly, and rigorous QA at Coherent. Discover how these ensure the performance and reliability of our optics and minimize supply chain risks and uncertainties.